Shop All
Frequently Asked Questions
Balance Macronutrients: Ensure a proper balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to provide fuel and support muscle function.
Prioritize Carbohydrates: Focus on complex carbohydrates from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables for sustained energy.
Pre-Exercise Nutrition: Consume a balanced meal or snack rich in carbohydrates and moderate in protein before workouts to fuel your session.
Fuel During Exercise: Consider easily digestible carbohydrates like energy gels or sports drinks for prolonged or intense workouts.
Adequate Protein Intake: Consume enough high-quality protein from lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy, legumes, or plant-based sources for muscle repair and growth.
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated by drinking fluids regularly, especially before, during, and after exercise.
Recovery Nutrition: Consume a mix of carbohydrates and protein after exercise to replenish glycogen stores and support muscle recovery.
Individualize and Experiment: Find what works best for you by paying attention to your body’s response to different foods and eating patterns.
Remember to seek guidance from a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist for personalized advice based on your specific needs and goals.
Hydration is highly important in sports nutrition as it directly impacts performance and overall well-being. Here’s why it matters:
Performance and Endurance: Proper hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal physical performance and endurance during exercise. Even mild dehydration can impair performance, reduce stamina, and hinder cognitive function.
Temperature Regulation: Hydration helps regulate body temperature, preventing overheating and reducing the risk of heat-related illnesses that can impact performance.
Energy Production: Water is essential for converting carbohydrates and fats into usable energy. Inadequate hydration can compromise energy production, leading to decreased performance and fatigue.
Nutrient Delivery and Waste Removal: Hydration supports the delivery of nutrients to muscles, aiding in their function, repair, and recovery. It also helps remove waste products from metabolic processes, reducing muscle fatigue and cramping.
Cognitive Function: Dehydration can impair cognitive function, affecting focus and decision-making abilities. Optimal hydration supports mental clarity during sports activities.
Recovery and Injury Prevention: Proper hydration is essential for post-exercise recovery, facilitating nutrient absorption, muscle repair, and waste removal. It can also reduce the risk of muscle cramps and dehydration-related injuries.
Monitor urine color as an indicator of hydration status, and drink fluids regularly throughout the day. For intense or prolonged exercise, consider electrolyte-rich fluids or sports drinks to replenish electrolytes lost through sweat. Consulting with a sports nutritionist or registered dietitian can provide personalized hydration recommendations based on individual needs.
The specific nutritional needs for your sport or activity can vary depending on factors such as the intensity, duration, and type of exercise you engage in. Here are some general guidelines for common sports and activities:
Endurance Sports (e.g., running, cycling, swimming):
Carbohydrates: Focus on consuming an adequate amount of carbohydrates to fuel endurance activities and maintain glycogen stores. This may involve consuming a higher percentage of carbohydrates in your overall diet.
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated before, during, and after exercise. Consider electrolyte replenishment for longer workouts or in hot environments.
Recovery: Include carbohydrates and proteins in your post-workout meals or snacks to replenish glycogen stores and support muscle recovery.
Strength and Power Sports (e.g., weightlifting, sprinting):
Protein: Ensure sufficient protein intake to support muscle repair, growth, and strength. Consume protein-rich foods with each meal and consider post-workout protein supplementation.
Carbohydrates: While protein is important, don’t neglect carbohydrates. They provide the energy needed for intense workouts.
Hydration: Hydrate adequately to support performance and recovery. Water is generally sufficient for most strength and power activities.
Team Sports (e.g., soccer, basketball):
Balanced Nutrition: Focus on a well-rounded diet that includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
Timing: Plan meals and snacks around training sessions and games to provide sustained energy and support recovery.
Hydration: Stay hydrated before, during, and after practices or games. Consider electrolyte-rich fluids for prolonged or intense activities.
Individualized Sports (e.g., gymnastics, martial arts):
Energy Balance: Ensure you’re meeting your energy needs to support the demands of your sport while maintaining a healthy body composition.
Nutrient Density: Opt for nutrient-dense foods to provide the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants for overall health and performance.
Injury Prevention: Pay attention to proper nutrition for bone health, muscle function, and injury prevention, as these sports often involve repetitive movements or high impact.
It’s important to note that these guidelines provide a general overview, and individual needs can vary. Consulting with a sports nutritionist or registered dietitian who specializes in your specific sport or activity can provide personalized recommendations based on your goals and requirements.
Revive Hydration Sticks

Bone & Joint Health
Bone & Joint Health
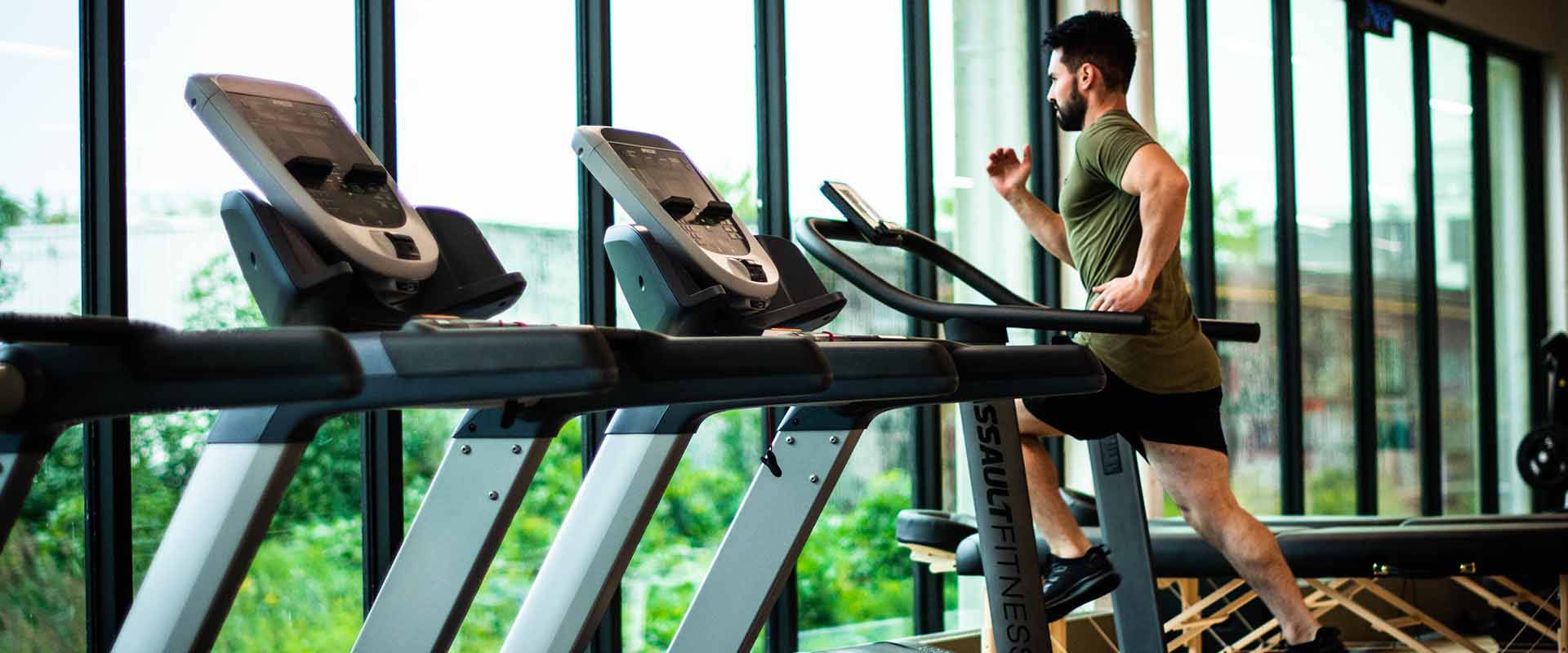
Cardio Health
Cardio health plays a critical role in an athlete’s performance and overall athletic ability. Improved endurance, faster recovery, increased stamina, better performance at high altitudes, and overall health and well-being are some of the key benefits of maintaining good cardiovascular health in sports.
Cardio Health
Cardio health plays a critical role in an athlete’s performance and overall athletic ability. Improved endurance, faster recovery, increased stamina, better performance at high altitudes, and overall health and well-being are some of the key benefits of maintaining good cardiovascular health in sports.